In Addition
Vol 14 号 6
November / December 2023
1. Health article
Planning Macronutrients essential in a balanced diet
Physical body is annamaya kosha (food sheath). Body is transient. But you should nourish it, because only a properly nourished healthy body can support the pranamaya kosha (life sheath) and manomaya kosha (mind sheath). Pranamaya kosha helps in the balanced flow of prana (life force) in the body.”…Sathya Sai Baba1
Introduction: The key attribute of health is “a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being”.2 Sustainable good health commands appropriate and adequate diet, exercise, rest and sleep, satisfying occupation, and recreation along with mental peace right from childhood. In this, a balanced diet of macro and micronutrients plays a predominant role. This article delves into the essential macronutrients.
1. What are macronutrients?
1.1 Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats as a group (CPF) are called “macronutrients” (in short “macros”) which the body does not produce but are absolutely necessary for it to function optimally. 
 Carbohydrates (carbs) are the primary source of energy crucial for the central nervous system, brain, and muscles. Protein is vital for building and repairing the tissues, producing enzymes to regulate metabolism, and transporting nutrients throughout the body. Amino acids in protein allow the immune system to form antibodies to fight infections. Fats are the energy reserve for the body, provide the essential fatty acids, insulate the body from extreme temperatures, and maintain healthy hormonal balance.3,4,5
Carbohydrates (carbs) are the primary source of energy crucial for the central nervous system, brain, and muscles. Protein is vital for building and repairing the tissues, producing enzymes to regulate metabolism, and transporting nutrients throughout the body. Amino acids in protein allow the immune system to form antibodies to fight infections. Fats are the energy reserve for the body, provide the essential fatty acids, insulate the body from extreme temperatures, and maintain healthy hormonal balance.3,4,5
1.2 CPF ratio: There cannot be one ideal carbs-protein-fat ratio. The proportion in which they should be included in a balanced diet is to be planned within the broad framework of 40-65% carbs, 10-35% protein, and 20-35% fat, with a 10% ceiling on saturated fats, based on one’s total calorie needs, after taking into consideration one’s age, gender, body composition, weight, occupation, lifestyle, and state of health. As an example, it could be 50-20-30 for an average healthy adult, 45-25-30 for those over 60’s, and 40-40-20 if the aim is weight loss.3,4,5
2. Our energy needs – Know the basics
2.1 What is a calorie? It is a measure of energy released by food when it gets metabolised. It is normally expressed in kilocalories (since calorie is too small a unit) written as kcal or Calorie (Cal for short). Our body extracts energy from carbs, protein, and fat like a car does from petrol. Carbs and proteins produce 4 Cal per gram, whereas fat gives 9 Cal per gram.4,5,6
2.2 Calorie needed per day ranges from 1600-2400 Cal for women and 2000-3200 Cal for men per day.6-8
2.3 Work out: The minimum level of energy required to sustain vital functions like breathing, digestion, and circulation depends on your weight, height, age and the level of your physical activity ranging from sedentary to very active lifestyle. This can be worked out using the formulae given in the links. 6-8
3. Choosing healthy Carbs
3.1 Carbs consist of sugar, starch, and fibre, and are the most abundant and widespread organic substance in nature formed by green plants and found in a wide array of foods. Sugar is a simple 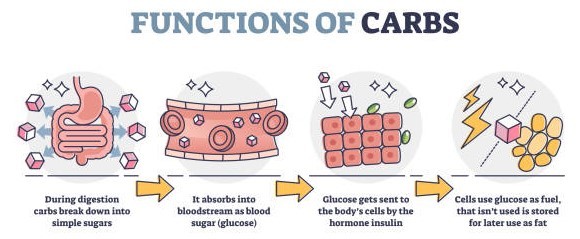 carb and gives instant energy. It includes fruit sugar (fructose), table sugar (sucrose), and milk sugar (lactose), naturally occurring in fruits, vegetables, milk, and milk products. Starch and fibre are complex carbs found in fruits, vegetables, grains, and cooked dry beans and peas; they give fullness, strengthen the body, and keep it energised for long. Most fruits are fibre-rich but bananas and dates are high in starch.9,10
carb and gives instant energy. It includes fruit sugar (fructose), table sugar (sucrose), and milk sugar (lactose), naturally occurring in fruits, vegetables, milk, and milk products. Starch and fibre are complex carbs found in fruits, vegetables, grains, and cooked dry beans and peas; they give fullness, strengthen the body, and keep it energised for long. Most fruits are fibre-rich but bananas and dates are high in starch.9,10
3.2 Most people’s diet is carb-rich, the proportion of starch being 50% in Western countries and up to 80% in Asia and Africa based on their major food sources and customs. But, carb is the only macro with no established minimum requirement though it is the body’s preferred fuel source. 275 g of carbs per day is recommended though lesser intake may help in reducing blood sugar and prevent hormonal imbalance.5,9,11-14 One can keep track of one’s intake with guidance from the carb list with portion size for each item, given in the links.13-19
Caution: Too much of simple carbs can cause a spike in insulin to balance the excess sugar released into the blood stream; extra carbs get stored as fat and increase the belly fat, may also retain water in the body causing bloating and gas.20,21
3.3 Fibre-rich foods: Fibre is present exclusively in plant foods in their cell walls. When soluble fibre, present in fruits, oatmeal, chia seeds, and lentils, gets dissolved in gastrointestinal fluids from stomach and intestine, it forms a gel-like substance which is digested in the large intestine. This improves overall digestion, prevents fats from being absorbed, and reduces blood cholesterol and sugar. Fermentable fibre, in some beans, legumes, raw banana, and leeks, onion and garlic, feeds healthy gut bacteria. (Resistant starch found in cooked and cooled rice and potatoes, green bananas, various legumes, cashews, and raw oats work similar to fermentable fibres). Insoluble fibre found in wholegrains, green beans, unpeeled potatoes, and most nuts and seeds, remains unchanged as it moves through the digestive tract, does not release calories but works as a bulking agent and facilitates easy bowel movement. For adults at least 20-35 g of fibre per day is advisable, but for above 50’s the need is slightly less; for children aged 2-5, it is 15 g, to be increased gradually over the years. One cup each of rice and lentils and some fruits and vegetables should fulfil the daily need of fibre. Taking a wide variety of fibres is known to reduce the risk of bowel cancer.22-30
Caution: Too much fibre can make one too full preventing both absorption and intake of other essential nutrients and may result in bloating, gas, and constipation.23
4. Choosing Protein rich food
4.1 Protein is found in every part of our body and its tissues. Our body makes protein from twenty-plus building blocks called amino acids (of which 9 are essential as body can’t make them) derived from food items. The recommended minimum daily intake for an average sedentary adult is 0.8 g/kg of body weight or 0.36 g/pound, to prevent getting sick. Adequate protein in every meal will ensure healthy hair, glowing skin, and lower the risk of arthritis.4,12,31-33
4.2 Eggs are favoured worldwide as a high protein food, with 6 g in one egg. But studies show that commercially sold eggs are not healthy and make people resistant to antibiotics as commercially reared hens live in adverse conditions and are injected with antibiotics to prevent them from falling sick. Plant-based quality protein comes from seeds and nuts (eg, walnuts, almonds, pecans, a handful has 6 g), cooked legumes (peanuts, beans, lentils, easily absorbable when cooked with cumin seeds and bay leaf), dry roasted gram and its powder, quinoa, oats, whole soya, vegetables like spinach, potato, sweet potato and broccoli. Dairy-based sources are A2 milk (10 g/cup), cottage cheese (11.5 g/100 g), and yogurt (8.5 g/cup), preferably fresh and homemade.31-37
4.3 Whereas it is good to consume the required amount of daily protein, it is best to space it over a day’s meals.31
Caution: Excess protein intake can lead to renal disorder and calcium loss through urine. If taking less protein, which normally vegetarians do, increase it gradually so that the body gets used to it, otherwise it may lead to abdominal discomfort. If supplementing with protein powder, choose the one without additives; it should not exceed 10% of the daily requirement.36,38
5. Choosing healthy Fats
If you need a diet of 2000 Cal/day, your total fat should not exceed 70 g (= 630 Cal @ 9 Cal/g). If you need to lose weight, fat should be much less. Focus on healthy fats from plant foods like nuts esp. walnuts, seeds esp. flax and chia, legumes, sprouts, avocado, and spinach. Take minimal saturated fats mostly found in dairy products, not more than 5-10% of total calories. Studies show that saturated fat from coconut is beneficial.12,37,39-44
Caution: Avoid harmful trans fats found mostly in packaged, fried, and baked foods.
6. Tips for balancing macronutrients
- It is more important to get your macros from different types of healthy foods rather than get obsessed with the numbers or grams consumed.12
- Choose a healthy plate with vegetables (excluding potatoes) and fruits filling ½ the plate, and whole grains ¼, the remaining ¼ should contain protein-rich foods like legumes and peanuts, nuts, and seeds, preferably soaked or dry roasted. Adults should eat at least 1 to 2 cups of fruits and 2 to 3 cups of vegetables per day.5,12,18,19,44
- Stop when you feel half or a little over half full and satisfied; resist the temptation to take more.
- In order to clean the system, melt extra fat, aid digestion, and ease bowel movement, drink reasonably hot water early morning and between meals, fresh aloe vera-amla-ginger juice, overnight soaked barley water, and include cabbage in diet.45
- Read carefully nutrition information on packaged foods. Avoid fast foods, processed and canned foods and drinks with high fructose, and refined sugar.10,12,13
- Do not resort to low carb or high protein diet or keto diet that centres on fat by yourself, unless medically advised, eg, keto diet is primarily used to help reduce the frequency of epileptic seizures in children.46


Final word: Preferred sources of macros should mostly be plant-based whole foods and not supplements. As always, everything in moderation; changes in diet should be relevant and gradual, giving time for the body to adapt.
References and Links
- Sri Sathya Sai Speaks on “Nature of Self”, Divine Discourse, Kodaikanal, 28 April 1999: sss32p1-13.pdf (sssbpt.info)
- World Health Organization(WHO) Definition Of Health - Public Health
- What are macros: https://www.foodnetwork.com/healthyeats/healthy-tips/what-are-macronutrients
- What Are Macronutrients? All You Need to Know (healthline.com)
- Macronutrient ratios: Daily Diet Composition Charts for Carbs, Protein, and Fat (verywellfit.com)
- Recommended Calories: https://www.verywellfit.com/what-is-a-calorie-and-why-should-i-care-3496238
- Calories calculation: https://www.verywellfit.com/how-many-calories-do-i-need-each-day-2506873
- BMR: https://www.wikihow.com/Calculate-Basal-Metabolic-Rate
- What is a Carb: https://www.brittanica.com/science/carbohydrate
- Types of Carbs: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/carbohydrates/art-20045705#
- No minimum carbs prescribed: https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5996878/
- Body’s Preferred fuel source: Macronutrients: 3 Types of Food Your Body Needs Daily (verywellfit.com)
- RDA for carbs: https://www.myfooddata.com/articles/foods-highest-in-carbohydrates.php
- Carbs and Insulin response: How Many Carbs Should a Person with Diabetes Have? (healthline.com)
- Carbs list: https://www.med.umich.edu/1libr/MEND/CarbList.pdf
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/12-healthy-high-carb-foods
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323110
- Determining food portions for fruits: https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/support/healthy-living/healthy-eating/healthy-eating-toolkit/food-portions/fruit
- Portion of vegetables: https://www.eatforhealth.gov.au/food-essentials/how-much-do-we-need-each-day/serve-sizes#
- Blood Sugar Spikes: Symptoms and How to Manage Them (verywellhealth.com)
- Do Carbs Make Your Belly Fat? | Healthfully
- Fibre: https://www.usta.com/content/dam/usta/pdfs/USTAFiber.pdf
- Soluble vs. Insoluble Fiber: What’s the Difference? (healthline.com)
- https://medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319176#what-are-the-benefits-of-fiber
- https://hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/carbohydrates/fiber/
- Fibre - British Nutrition Foundation
- What Are High Fiber Foods? Chart, Fiber Needs, and More (healthline.com)
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/high-fibre-foods/
- The Top 25 Fruits High In Fiber - Nutrition Advance
- https://healthline.com/nutrition/resistant-starch-101#how-to-add
- Protein: https://hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/what-should-you-eat/protein/
- Essential Amino acids: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/22243-amino-acids
- 5 Amazing vegetarian protein foods better than egg—fit tuber: https://youtube.com/watch?v=Pcd28t9x8w87t=459s
- https://hopkinsmedicine.org/wellness-and-prevention/5-protein-packed-foods-for-healthy-meatless-meals
- https://pharmeasy.in/blog/list-of-protein-rich-food-for-vegetarians/
- How much protein you need for weight loss: How much PROTEIN do you need for weight loss? - YouTube
- Fat and Protein in fruits: Fruits Protein And Fruits Fat Content (dailyonefruit.com)
- Excess protein: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9614169
- Track your fats: https://newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org/discussion/fat-grams-how-to-track-fat-in-your-diet/
- Healthy fats: https://helpguide.org/articles/healthy-eating/choosing-healthy-fats.htm
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/what-should-you-eat/fats-and-cholesterol/
- Goodness of coconut oil: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/food-features/coconut-oil/
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/healthy-cooking-oils#TOC_TITLE_HDR_3
- Healthy Eating Plate | The Nutrition Source | Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
- Melt extra fat: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gjYVS8m91UU
- Should you try the keto diet? - Harvard Health
2. UK annual meet, London, 24 September 2023
This national meet organized by the UK coordinator 02822 was attended by 21 practitioners in person and 8 participated virtually. All material presented in the seminar was sent in advance to the coordinator who circulated this to all UK practitioners.
In his address, Dr Aggarwal shared that ever since Vibrionics was started with Swami’s blessings in 1994, UK has been in the forefront of vibrionics seva. He encouraged the gathering to keep up the momentum by introducing more new people to take up this seva, from amongst their patients, friends, relatives, and Sai Centres. He also made a plea that more practitioners come forward to take up admin work to lighten his and UK coordinator’s workload. It was very encouraging that practitioner 03531 who is already doing a lot of IT work offered to take greater responsibility. The practitioner 02802 made a very welcome suggestion that we should be open to recruiting non-practitioners for admin seva; full training will of course be provided.
There were two PowerPoint presentations*; the first was made by guest speaker Dr Bishakha Chowdhury on ‘Real-life management of type-2 diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol’. Each of these three conditions, if untreated, is life-threatening in itself. They often co-exist and together they vastly increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. Emphasis was placed on prevention by simple practical lifestyle management. She recommends diet, low in sugar, carbs, salt and saturated fats, high in fibre with more pulses and legumes and good fluid intake (two litres of water/day) which reduces hunger. Regular exercise will reduce weight, BP, strain on the heart, and stress. Regular meal times are important, so is eating before 8 pm.
The other presentation was given by our experienced SVP 02802 on ‘Life-threatening Medical Emergencies’. From her experience as a GP for 33 years she emphasized ‘Awareness can be lifesaving’. As such, she explained the following emergency conditions which need urgent medical care: unconsciousness or chest pain for over 30 minutes, breathing difficulty, serious blood loss, signs of shock, sepsis, or meningitis, acute allergic reaction, sudden severe headache, severe burns and choking. She gave useful tips on how to recognise an emergency and how to deal with such situations until help arrives.
The coordinator concluded with a reminder to the practitioners to continue using the IB remedy. He regularly sprinkles the IB around his house and garden and believes this has helped to keep these areas clean. Eight practitioners had the opportunity to recharge their 108CC boxes.
*Full details in PowerPoint format are available on request from [email protected]
3. Group activities gain momentum under Sai Vibrionics Institute for Research and Training ( SVIRT)
Camps
With the untiring effort of RCs and enthusiastic participation by local practitioners, undeterred by heavy rains, just in seven months to the end of Sept 118 practitioners held 968 camps at 97 venues including 17 new venues in Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh & Telangana, and Gujarat. Other states where camps are held, are Kerala, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Delhi, Haryana, UP, Uttarakhand, Tamil Nādu, West Bengal & Odisha. Camps are generally held monthly and in many places, weekly depending upon the local demand. A total of 32837 patients received treatment. This momentum is expected to be maintained more vigorously in the future.
Participation in the Prema Tharu Tree Plantation Initiative
Between 16 Sept and 14 Oct 2023, a total of 278 saplings under Vibrionics care were planted in the northern region of India with the participation of eight practitioners, Bal Vikas children, seva dals, and local residents. For a strong foundation, CC1.2 Plant tonic is used at the time of planting, and later other appropriate remedies for protection and care. So far, 278 saplings have been planted in four states of India - 232 in Delhi, 38 in Haryana, 5 in UP, and 3 in Uttarakhand. This is just the beginning as SVIRT is committed to supporting activities related to the protection of our environment.
Clinic in Puttaparthi
A regular clinic is held twice a week at the office of SVIRT by local and visiting practitioners.

4. Anecdote
Sai grace on terminally-ill patient 03598…UK
A 93-year-old widower, a close family friend, lived alone with support from neighbours and friends. He enjoyed reasonably good health other than osteoarthritis of his knees and cervical spine. He was receiving regular steroid injections into his knees with partial relief. He was coping independently reasonably well until March 2023 when he fell in the bathroom, suffered severe hypothermia, and was admitted to the hospital. This started a series of crises with recurrent urinary and chest infections and a progressive decline in his general health. He became completely bed-bound with severe exacerbation of his arthritis. Both his knees were swollen and a mere touch would make him scream with pain! He was put on strong opiate analgesics which made little difference to his pain.
He had a prolonged stay in hospital due to various infections and hope for recovery was waning. He became increasingly drowsy, refusing to eat, and responded poorly to commands even after finishing two courses of antibiotics. The pain was so severe that he would scream with every little movement of his legs despite strong medications. As a desperate measure to help relieve his pain the practitioner, a recently retired physician, prepared the following remedy:
CC12.1 Adult tonic + CC20.2 SMJ pain + CC20.3 Arthritis + CC20.4 Muscles and soft tissues + Pain* + Inflammation**…in water orally and in castor oil for topical application
On 3 June, she gave him one dose in the mouth and discreetly applied the remedy oil to both his knees chanting Swami’s name. She also added three pills to the jug of drinking water by his bedside. Both medical and general opinion was that his end was only days away. But this was not to be! When she went back to visit him two days later, to her absolute astonishment, the patient was fully alert, comfortable in bed and was able to make perfect and sensible conversation. He denied feeling any pain in his knees. There was no swelling and the joints were not tender anymore. When checked with the nursing staff, there has been no change in his medications to explain such a dramatic turn-around in his condition. He was discharged to a care home in mid-June where he spent his last three weeks in peace and passed away painlessly on 7 July 2023
*Pain: NM20 Injury + NM36 War + SR397 Morphinum + Cannabis 10M + Cocaine 10M + Crotalus Horridus 30C + Lithium 10M, all four from homoeo store
**Inflammation: NM45 Atomic Radiation + NM113 Inflammation + SM2 Divine Protection + SM5 Peace & Love Alignment + SM6 Stress + SR324 X-ray + SR348 Cortisone
5. In Memoriam
Mrs Chandravati Vaman Shetty12017…India, our vibrant and multi-faceted 74-year-old VP from Mumbai, reached Swami’s Lotus feet on 1 Aug 2023 after a 10-month-long valiant battle with subarachnoid haemorrhage. Since 2011 she had been a very active practitioner, treating patients regularly at Sion and Wadala medical camps travelling long distances, till she was admitted to the hospital. She was a much-adored Bal Vikas Guru, a soulful bhajan singer, a regular seva dal at Prasanthi Nilayam and participated with great dedication, devotion and enthusiasm in all samiti activities, inspiring everyone with her beautiful smile and cheerful demeanour. She is fondly missed by both her family and Sai family.
